Introduction
As many of us know, working with chemicals can be dangerous. That’s why it’s crucial to understand and properly read a GHS Safety Data Sheet (SDS). An SDS is a document that provides information about the hazards of a chemical and how to work safely with it. It’s important to know that SDSs are not just for industrial settings. These documents can also be found in schools, laboratories, and even in households. So, whether you’re a scientist, a janitor, or a DIY enthusiast, it’s important to know how to read an SDS. GHS Safety Data Sheets (SDS) are an important tool for anyone working with chemicals. They provide detailed information on the hazards and safe handling of a chemical, and are a crucial resource for staying safe in the workplace. In this article, we will take a closer look at the different sections of a GHS SDS and what information they contain.
The Globally Harmonized System (GHS) for Hazard Communication – On June 1, 2016, the Globally Harmonized System (GHS) format became mandatory for all containers of hazardous chemicals.
Reference: https://unece.org/ghs-rev2-2007
Some of the changes that may be made to an SDS to bring it into compliance with GHS include:
- Adding a standardized 16-section format for the SDS, including sections for identification, hazards identification, composition/information on ingredients, first aid measures, fire-fighting measures, accidental release measures, handling and storage, exposure controls/personal protection, physical and chemical properties, stability and reactivity, toxicological information, ecological information, disposal considerations, transport information, and regulatory information.
- Using standardized hazard statements, precautionary statements, and pictograms to clearly communicate the hazards of the chemical.
- Providing more detailed information on the composition of the chemical, including information on impurities and stabilizing additives.
- Updating the SDS to include new toxicity data and environmental data, if available.
- Adding new information on safe handling and storage procedures, as well as emergency response procedures.
These are some of the main changes that may be made to an SDS to bring it into compliance with GHS. The specific changes required will depend on the chemical and the country or region where it is used.
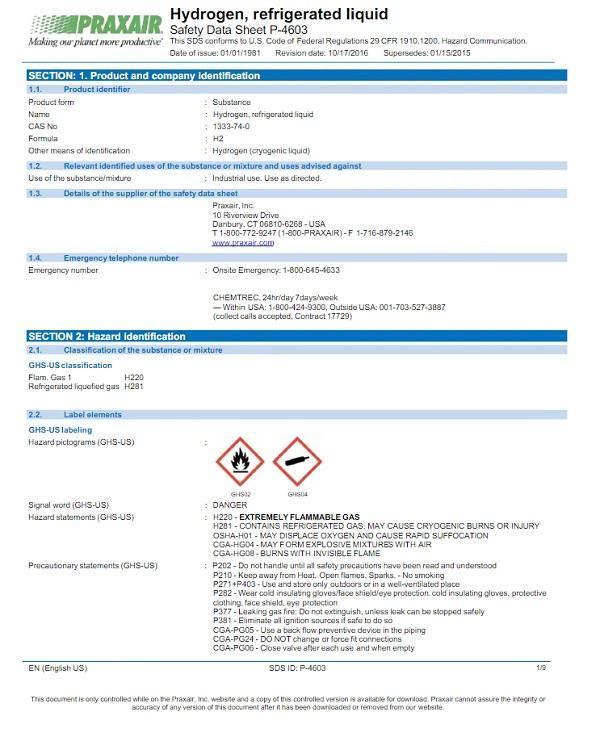
Image of an Example of a GHS Safety Data Sheet:
How GHS SDSs are Organized
Data thats likely to be needed in a hurry such as a material’s name, composition, hazards, safety precautions, and emergency procedures is presented in the first six sections. Information on safe handling and storage procedures is located in the middle of the SDS, followed by more specialized, technical information toward the end.
All of the data in GHS Safety Data Sheets is presented in clear, non-technical language, and standard phrasing, so it’s easy for people who work with hazardous materials to get the information they need when they need it.
Section 1: Identification
The first section of a GHS SDS is the identification section. This section includes the product identifier, which tells you the name and manufacturer of the chemical. It also includes the manufacturer or distributor’s name, address, and phone number, as well as an emergency phone number that you can call in case of an emergency. This section also includes the recommended use of the chemical and any restrictions on its use.
Section 2: Hazard(s) Identification
The second section of a GHS SDS is the hazard identification section. This section includes all hazards related to the chemical, including health hazards, flammability, reactivity, and any other hazards that may be present. This section also includes the required label elements, such as the signal word, hazard statements, and pictograms. This information is crucial for understanding the chemical’s hazards and how to work with it safely.
Section 3: Composition/Information on Ingredients
The third section of a GHS SDS is the composition and information on ingredients section. This section includes information on the chemical ingredients of the product, including their concentrations. This section also includes any trade secret claims that the manufacturer may have for certain ingredients. This information is useful for understanding the chemical’s hazards and how to work with it safely.
Section 4: First-Aid Measures
The fourth section of a GHS SDS is the first-aid measures section. This section includes important information on the symptoms and effects of exposure to the chemical, both acute and delayed. It also includes the required treatment for exposure to the chemical. This information is crucial for responding to an emergency and providing the necessary first-aid.
Section 5: Fire-Fighting Measures
The fifth section of a GHS SDS is the fire-fighting measures section. This section includes information on suitable extinguishing techniques and equipment for the chemical, as well as any chemical hazards from fire. This information is crucial for responding to a fire emergency involving the chemical.
Section 6: Accidental Release Measures
The sixth section of a GHS SDS is the accidental release measures section. This section includes emergency procedures, protective equipment, and proper methods of containment and cleanup in case of an accidental release of the chemical. This information is crucial for responding to an accidental release of the chemical and keeping yourself and others safe.
Section 7: Handling and Storage
The seventh section of a GHS SDS is the handling and storage section. This section includes precautions for safe handling and storage of the chemical, including information on incompatibilities with other chemicals. This information is crucial for preventing accidents and keeping yourself and others safe while working with the chemical.
Section 8: Exposure Controls/Personal Protection
The eighth section of a GHS SDS is the exposure controls and personal protection section. This section includes information on OSHA’s Permissible Exposure Limits (PELs) and Threshold Limit Values (TLVs) for the chemical, as well as appropriate engineering controls and personal protective equipment (PPE) that should be used when working with the chemical. This information is crucial for protecting yourself from exposure to the chemical.
Section 9: Physical and Chemical Properties
The”Physical and Chemical Properties” section provides important information about the chemical’s characteristics. This section includes information such as the chemical’s appearance, odor, pH, melting point, boiling point, flash point, and density. It also includes information about the chemical’s solubility in water and other solvents, as well as its vapor pressure and density. Additionally, the section may include information about the chemical’s stability, such as whether it is stable, unstable, or reactive under certain conditions. This information can be critical for understanding the safety risks associated with handling and using the chemical, as well as for determining appropriate storage and handling procedures.
Section 10: Stability and Reactivity
This section provides information about the chemical’s stability and the potential for hazardous reactions. This section includes information about the chemical’s reactivity, including conditions to avoid, such as high temperatures or exposure to certain chemicals. It also includes information about the chemical’s stability, including whether it is stable under normal conditions, or if it is a reactive chemical that may pose a risk if not handled properly. Additionally, this section may include information about the chemical’s potential for polymerization, or the likelihood of it undergoing a chemical reaction that creates a large, complex molecule. This section is important for understanding the chemical’s behavior and taking the necessary precautions to prevent accidents or dangerous reactions.
Section 11: Toxicological Information
This section includes information about the potential toxic effects of the chemical on human health. This section includes information about the routes of exposure, such as inhalation, ingestion, and skin contact, as well as the related symptoms and effects, both acute and chronic. It also includes numerical measures of toxicity, such as LD50/LC50 values, which are used to measure the dose at which a chemical will cause death or other harmful effects in a certain percentage of test animals. This section is important for individuals who may be handling or using the chemical, as it provides information on the potential health hazards and how to avoid exposure. It also provides guidance to medical professionals in case of exposure and emergency situations.
Section 12, Ecological information
This section provides information on the chemical’s impact on the environment, including its effects on plants, animals, and aquatic life. This section also includes information on the chemical’s persistence and degradability in the environment, as well as any bioaccumulation potential. This information is important for those who handle or transport the chemical, as well as for those who are responsible for its disposal.
Section 13, Disposal considerations
This section provides information on the proper methods for disposing of the chemical, including any regulations or guidelines that must be followed. This section also includes information on the chemical’s reactivity and stability, as well as any special precautions that must be taken during disposal.
Section 14, Transport information
This section provides information on the regulations and guidelines for transporting the chemical, including its proper shipping name, hazard class, and identification number. This section also includes information on any special precautions that must be taken during transport, such as the use of specific packaging or labeling.
Section 15, Regulatory information
This section provides information on any regulations or laws that pertain to the chemical, including information on any restrictions on its use or disposal. This section also includes information on any international or national regulations that apply to the chemical.
Section 16, Other information
This section includes the date of preparation or last revision of the Safety Data Sheet. This section also includes any additional information that may be relevant to the safe handling and use of the chemical, such as its supplier or distributor.
Conclusion
A GHS Safety Data Sheet (SDS) is an important tool for anyone who works with chemicals. It provides detailed information on the hazards, handling, and disposal of a chemical, as well as any regulatory requirements that must be followed. By understanding the information contained in an SDS and following the recommended precautions, you can ensure the safe handling and use of chemicals in the workplace. Always make sure to have an updated SDS available and accessible in case of an emergency.